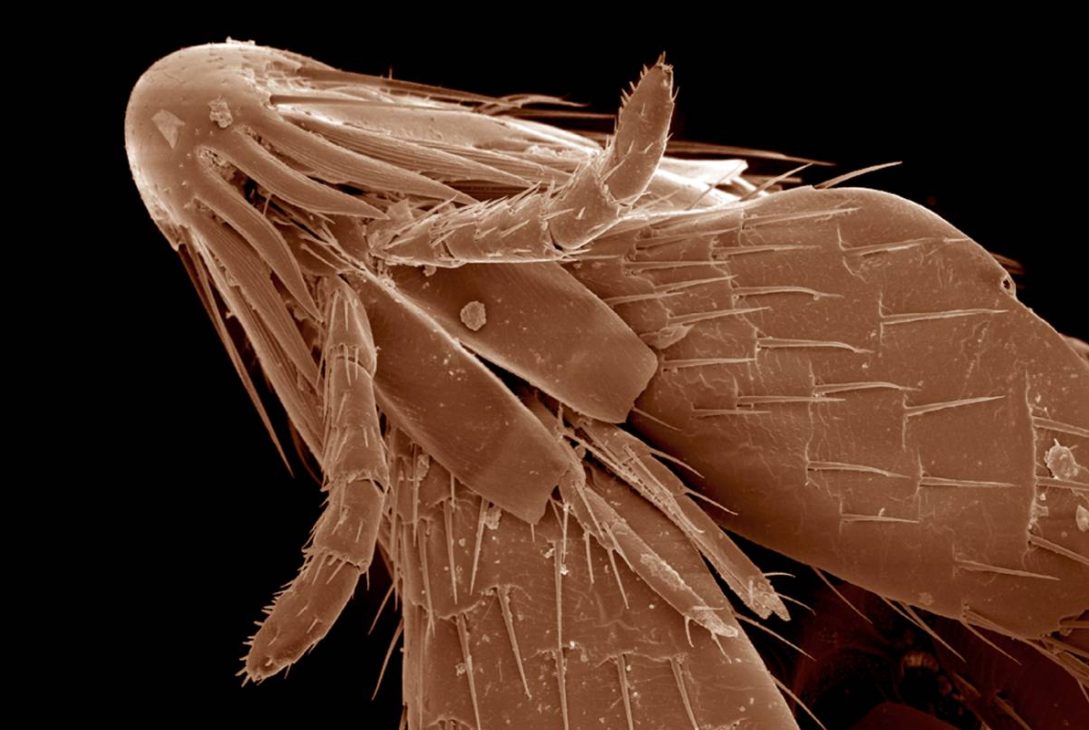
Fleas are these small, wingless bugs that love to feast on the blood of birds and mammals, including humans. You’ve probably heard of them causing havoc on pets like cats and dogs, but they can also end up biting you and causing some health problems.
It’s important to know how fleas can affect your health so you can keep them under control and prevent any issues from arising.
Flea Bites and Skin Reactions
When fleas bite humans, they inject saliva into the skin to facilitate their feeding. This saliva contains various substances that prevent blood from clotting, making it easier for the flea to consume its meal. However, these substances can also trigger an allergic reaction in humans. This reaction often results in the appearance of itchy red bumps at the site of the bite, which are similar in appearance to mosquito bites.
For many people, flea bites are not just a minor annoyance but can be particularly bothersome. The intense itching that accompanies flea bites can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily activities. The severity of the reaction can vary from person to person, with some individuals experiencing only mild itching while others may suffer from more intense irritation.
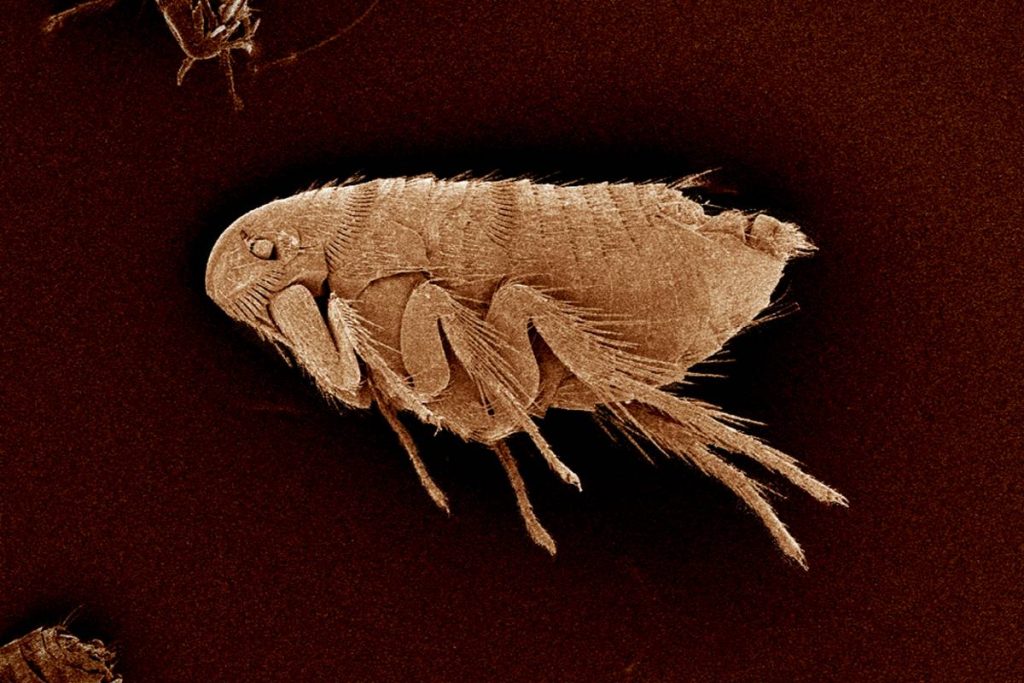

The discomfort from flea bites often leads to scratching, which can exacerbate the problem. Scratching the bites can cause the skin to break, creating an entry point for bacteria. This increases the risk of secondary infections, which can complicate the initial reaction to the flea bites. Infected bites may become swollen, filled with pus, and more painful, requiring medical attention to properly treat the infection and prevent further complications.
Moreover, for individuals with more sensitive skin or those who are allergic to flea saliva, the reaction can be more severe. These individuals may develop larger, more inflamed welts that can take longer to heal. In some cases, people might experience a condition called flea allergy dermatitis, where the allergic reaction extends beyond the bite site and causes widespread skin irritation and discomfort.
To mitigate the effects of flea bites, it’s important to avoid scratching and to keep the affected area clean. Over-the-counter antihistamines and anti-itch creams can help alleviate itching and reduce the risk of secondary infections. If bites become severely infected or if there is a pronounced allergic reaction, seeking medical advice is essential to ensure proper treatment and care.
Allergic Reactions
Beyond the typical itching and redness, some individuals may experience more severe allergic reactions to flea bites. This condition, known as flea allergy dermatitis, is more common in pets but can also affect humans. Flea allergy dermatitis occurs when the immune system reacts strongly to the flea’s saliva, causing a more intense and widespread reaction than the usual minor irritation.
Symptoms of Flea Allergy Dermatitis
- Hives: Raised, red, and itchy welts on the skin.
- Swelling: Puffiness and tenderness around the bite area.
- Severe Reactions: In extreme cases, symptoms like difficulty breathing can occur, indicating a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) that requires immediate medical attention.
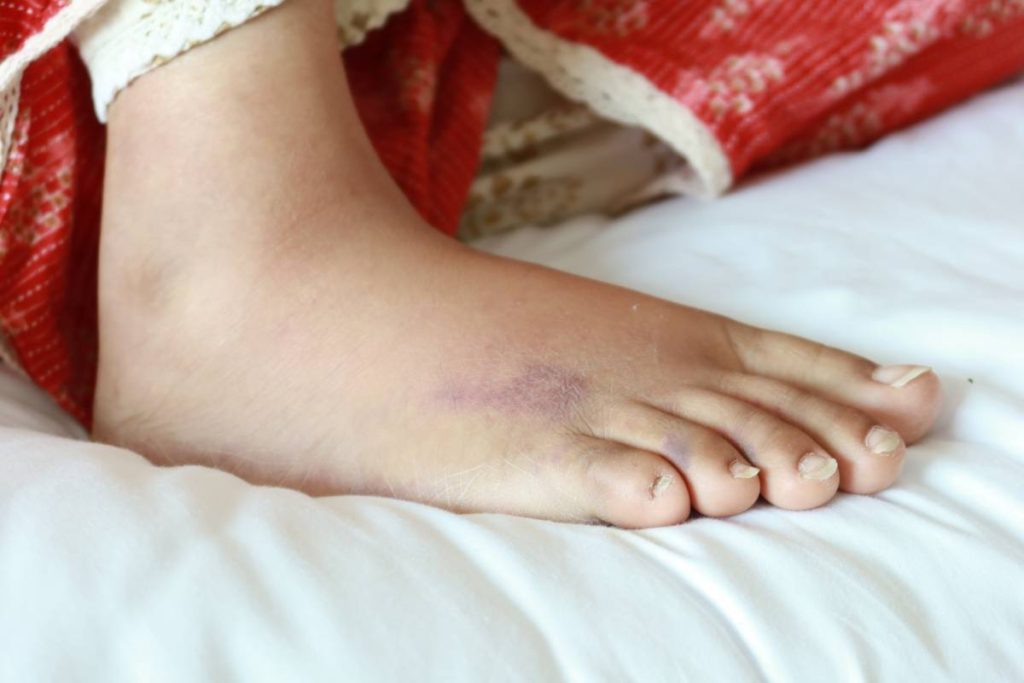
Who Is at Risk?
- Sensitive Skin: People with naturally sensitive skin.
- Pre-existing Allergies: Individuals who already have allergies are more prone to severe reactions.
Managing Flea Allergy Dermatitis
- Avoid Scratching: Scratching can break the skin and lead to secondary infections.
- Keep the Area Clean: Clean the bite area to prevent infections.
- Over-the-Counter Remedies: Use anti-itch creams or antihistamines to reduce itching and swelling.
- Cold Compresses: Apply cold compresses to soothe the affected area.
- Seek Medical Advice: For severe reactions, a healthcare professional may prescribe stronger medications like corticosteroid creams. Carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) might be necessary for emergency treatment in cases of anaphylaxis.
Flea-Borne Diseases
Fleas are not just annoying; they can also transmit diseases. One of the most well-known diseases associated with fleas is the plague, caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Historically, the plague caused devastating pandemics, but it is now rare and treatable with antibiotics. Fleas become infected by biting infected animals, such as rodents, and can then transmit the bacteria to humans through bites.
Another disease spread by fleas is murine typhus, caused by the bacterium Rickettsia typhi. This disease is typically less severe than the plague but can still cause significant illness, with symptoms like fever, headache, and rash. Murine typhus is more common in areas with poor sanitation and high rodent populations.
Fleas can also carry tapeworms, which can infect humans, particularly children. This usually happens if a person accidentally ingests a flea-carrying tapeworm larvae, which can occur if they come into contact with flea-infested pets.
Preventing Flea Infestations
Preventing flea infestations is crucial for minimizing the risk to humans. Regularly treating pets with veterinarian-recommended flea control products is one of the most effective measures. These products can kill adult fleas and prevent eggs from hatching, reducing the overall flea population.
Keeping the home clean is also important. Vacuuming carpets, furniture, and pet bedding can help remove fleas and their eggs. Washing pet bedding and regularly grooming pets can further reduce the risk of infestations. In severe cases, professional pest control services may be necessary to eliminate fleas from the home environment.
What to Do If You Have Fleas

If you find fleas on yourself or in your home, it’s important to take action promptly to avoid discomfort and further infestation. Here are some steps you can take:
Immediate Relief for Flea Bites
- Use Over-the-Counter Treatments: Antihistamines and anti-itch creams can help alleviate the itching and discomfort caused by flea bites.
- Monitor for Infection: If bites become red, swollen, or start oozing, they might be infected. In this case, seek medical attention to get the appropriate treatment.
Addressing the Infestation
- Treat Your Pets: Fleas often come from pets, so it’s essential to treat them with veterinarian-recommended flea control products. This can help kill adult fleas and prevent new ones from hatching.
- Clean Your Home Thoroughly: Vacuum carpets, furniture, and pet bedding to remove fleas and their eggs. Wash pet bedding regularly in hot water to kill any remaining fleas.
- Use Flea Control Products: Consider using flea control products in your home, such as sprays or foggers, to eliminate fleas from your living environment.
Professional Help
- Consult a Veterinarian: For effective pet treatment, a veterinarian can recommend the best flea control products and provide guidance on preventing future infestations.
- Hire a Pest Control Specialist: For severe infestations, a pest control specialist can offer comprehensive solutions to eliminate fleas from your home.
Taking these steps can help you effectively manage and prevent flea infestations, ensuring a more comfortable and safe environment for you and your pets.
Conclusion
Fleas can pose a threat to humans, mainly through their bites which can cause allergic reactions and transmit diseases. Although the risks are minimal with the right precautions, it’s important to know how to prevent and control flea infestations to keep both people and pets healthy.
Taking proactive measures, like treating pets for fleas and maintaining clean living areas, can minimize the chances of flea issues and promote a healthier, more comfortable living space.